Cells (AQA AS Biology) PART 1 of 6 TOPICS
|
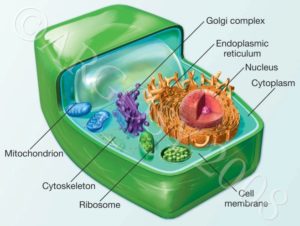
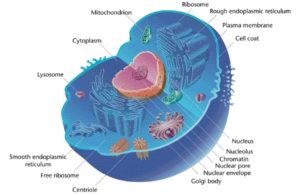
Structure of eukaryotic cells:
The ultra cellular structure of a eukaryotic cell (animals and plants)must be known with the functions of organelles:
- Cell surface membrane is selectively permeable to control the exchange and is mainly made up of lipids and proteins.
- Nucleus is enclosed of a membrane which is made of two membranes itself and is perforated by nuclear pores which controls the exchange between the cytoplasm and the nucleus. The nucleus contains chromatin which is the state of DNA when the cell is not dividing. A nucleolus is present in the nucleus which manufactures ribosomes.
- Mitochondria are cigar-shaped organelles and generate ATP by aerobic respiration. It has two membranes where the inner membrane is deeply folded to make cristae which maximises surface area. Between this membrane and the outer membrane there is a space called intermembrane space. The watery matrix in the middle contains enzymes, a circular loop of DNA and granules.
- Chloroplasts have an envelope of two membranes with a gel-like gelatinous matrix called the stroma. The stroma contains a system of membranes that contain photosynthetic pigments called thylakoid membranes are stacks of grana and lamellae as well having its own loop of DNA, enzymes and ribosomes.
- Sacs of the golgi apparatus are called cisternae. Newly formed membranes created on the ends of these sacs are called vesicles. Golgi apparatus is a processing and packaging structure and allows enzymes to be secreted via vesicles and also makes lysosomes.
- Lysosomes are membrane bound vesicles containing hydrolytic enzymes called lysozymes. These enzymes hydrolyse proteins, nucleic acids, lipids and carbohydrates and are made in the rough endoplasmic reticulum. Transport vesicles transport these enzymes to the golgi apparatus.
- Rough endoplasmic reticulum is involved in folding, modification and transport of proteins. It has ribosomes on its endoplasmic reticulum.
- Ribosomes are small organelles where protein synthesis occurs.
- Smooth endoplasmic reticulum is involved in lipid synthesis.
- Cell wall (only in plants) is made up of cellulose which is rigid and supports the cell.
- Vacuoles (only in plants) are full of fluid which is used to make the cell rigid, used as a storage and waste matter can be collected of decomposing complex molecules.
- Plasmodesmata (only in plants) are pores between two plant cells which help to transfer substances between cells
Eukaryotic cells have membrane bound organelles.