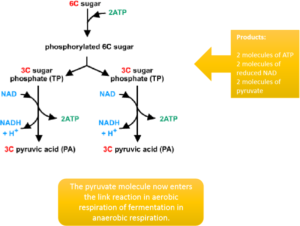
Glycolysis is the initial stage of both aerobic and anaerobic respiration.
It occurs in the cytoplasm of all living cells and is the process by which a hexose sugar, usually glucose, is split into two molecules of the 3-carbon molecule, pyruvate.
There are four stages: