| Normal Flow: DNA, RNA, Protein | Retrovirus: RNA, DNA, RNA, Protein |
Virus Function
- Virus: small nucleic acid genome enclosed in capsid
- Penetrates cell → takes over metabolic machinery → assembles new virus copies
Virus Structure
- Nucleic Acid: either RNA or DNA which contains viruses information to make progeny
- DNA/RNA may be double-stranded or single-stranded
- Capsid: viral protein coat enclosing genome, determines genomes size/shape and specificity
- Viral envelopes: surrounds capsids, comes from host membranes lipids & proteins, help virus infect host
- The viral envelope mediates entry into the cell, the capsid enters the nuclear membrane, and the genome is all that enters the nucleus
- Antibiotics don’t work on viruses bcuz don’t have a cell wall that can be targeted
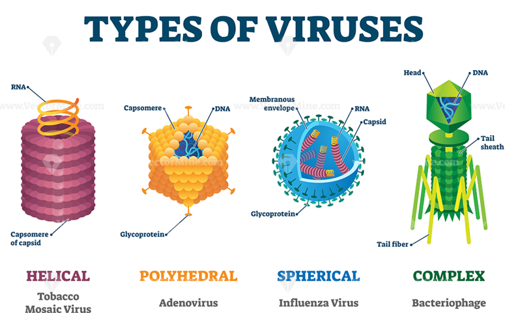
Types of Viruses
- Are specific for types of cell they parasitize: some attack only one kind of cell within single species and others attack similar cells from range of closely related species
- Bacteriophages: infect bacteria, most complex
- Simpler Viruses
- Viroids: infect plants, just floaty RNA (no capsids)
- Plant infections spread by plasmodesmata
- Prion: infectious misfolded proteins that can transmit incorrect shape
- Viroids: infect plants, just floaty RNA (no capsids)
Viruses and Evolution
- Rapid evolution bcuz produce many copies over short time & less proofreading → mutations can be passed on
- High rate of mutation increase pathogenicity bcuz host populations don’t evolve defense as fast as viruses evolve
- Viruses mutate and evolve quickly → new strains on regular/seasonal basis
- Genetic material of different but related viruses can combine when present in host cell → produce new virus
Living or Nonliving?
- Living characteristics: have DNA or RNA, can reproduce/replicate, metabolic activity, and genetic recombination but only in hosts cell
- Nonliving: are not cellular
Replication of Viruses
Lytic Cycle:
- Used by virulent viruses: builds viral DNA & proteins → self assemble into virus → viruses bust out of the cell and lyse it, releasing lots of viruses → KILLS HOST CELL
Lysogenic Cycle
- Viral DNA incorporated into the cell’s genome by genetic recombination → host cell duplicates viral DNA & proteins
- Used by temperate viruses DOES NOT KILL HOST CELL
- Prophage: viral genes inserted into a bacteria
- Provirus: viral genes inserted into an animal cell
- Stays dormant until there are optimal conditions, stress, or external environment stimulus (radiation or chemicals) → releases viruses to create an infection in the lytic cycle
- So cycle technically in between phase
RETROVIRUS SYNTHESIS:
- Retrovirus: ssRNA animal virus
- Glycoprotein plasma membrane of virus fuses with that of the cell (virus enters cell)
- The virus contains protein capsids, RNA, & reverse transcriptase which it releases into the cytoplasm of the host cell
- Reverse transcriptase makes DNA complement strand from RNA
- dsDNA strand transcribed immediately to manufacture mRNA (lytic) or be incorporated into the host genome (lysogenic)
- HIV: makes an envelope and leaves through exocytosis
Over time eats up the host’s membrane destroying the immune system