- “Evolutionary history of a species”
- Determined through fossils, homologous structures, morphology, & molecular biology
Taxonomy: classification of organisms; organisms are classified into categories called taxa
Hierarchical Classification
- Each taxon more inclusive than the other
- “Dumb Kings Play Chess On Fine Green Sand”
- Species: group of closely related organisms that can reproduce
- Genus: phylogenetically closely related species
- Family: Genera that share same features
- Order
- Classes:
- Phyla:
- Kingdom
- Domain
Phylogenetic Trees
- “Evolutionary history of an organism represented by a branching diagram” (Hypothesis!)
- Branch Point: represents common ancestry of 2 evolutionary lineages diverging from it
- Sister taxa: species that share immediate common ancestor not shared by other groups
- Represents a genus
- Basal taxon: group that diverges early on
- Tree shows pattern of descent, NOT phenotypic similarity
- Branch length = estimated amount of evolutionary change or time
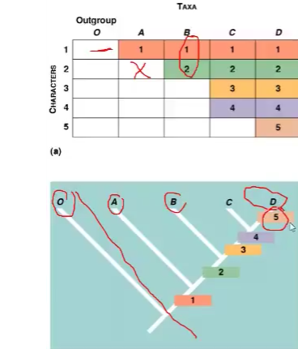
Cladistics
- Uses common ancestry and traits to place species into groups called clades
- Clades: ancestral species & all of descendents
- Cladogram shows relationships between diff organism from common ancestor
- Branches determined by comparing number of derived characters in each taxon
- More primitive = earlier branching
- Fewer derived = later branching
- Outgroup: species closely related but not part of the group we are studying (ingroup)
- Is the most divergent (different) and least closely related
- Branches determined by comparing number of derived characters in each taxon
- Node represents species → all three species are descended from it
Types of Clades
- Monophyletic: ancestral species & all of its descendents (best!)
- Paraphyletic: ancestral species & some of its descendents
- Polyphyletic: includes distantly related species but not recent common ancestor
Shared Ancestral & Shared Derived Characteristics
- Descent with modification has resulted in organisms with shared and diff characteristics from common ancestor
- Shared Ancestral: character that originated from ancestor of a taxon (ex: backbone)
- Derived: novelty unique to clade
- Can be loss or gain of a characteristic
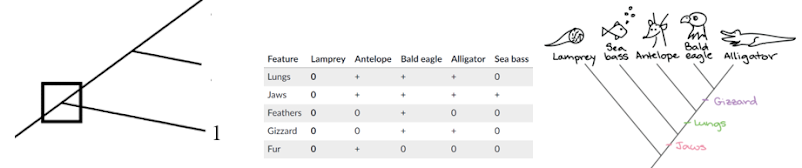
Maximum Parsimony: simplest explanation is usually most correct one
- Most parsimonious tree is the one with the less amount of changes
- This tree is less parisomus bcuz assumes that jaw evolved twice
Evolution and Genome
- Comparison of nucleic acids can show relatedness
- Ex: between humans and fungi
- Diff genes evolve at diff rates = molecular trees represent short/long period of time
- rRNA changes slowly→ investigate events that happened long time ago
- mDNA evolves rapidly→ investigate recent events
- Orthologous genes: homologous genes found is diff species as a result of speciation
- Paralogous genes: homologous genes in a species that results from gene duplication
- May diverge and take on new functions; useful cuz extra copy of genes permits modification w/o loss of original copy
- Pseudogenes: Paralogous genes that have lost function of coding for functional gene product (vestigial)
- Over evolution will have high mutations
- Nucleic acids are poorly conserved
- Conserved = few changes over time
- Poorly conserved homologous genes used to relate distant species
Molecular Clocks
- “Method of estimating past evolution events based on pattern of neutral mutations”
Mutations in genes make it accurate and natural selections makes inaccurate